L-Amino Acid Structures
Backbones are oriented amino(left) to carboxy(right)
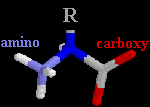

|
Rotate 180o: alanine ; valine ; leucine ; isoleucine Toggle dot surface: |
alanine (ala = A) |
valine (val = V) |
leucine (leu = L) |
isoleucine (ile = I) |
|
Rotate 180o: methionine ; proline ; phenylalanine ; tryptophan Toggle dot surface: |
methionine (met = M) |
proline (pro = P) |
phenylalanine (phe = F) |
tryptophan (trp = W) |
|
Rotate 180o: glycine serine ; threonine Toggle dot surface: |
glycine (gly = G) |
serine (ser = S) |
threonine (thr = T)) |
|
|
Rotate 180o: glutamine ; asparagine ; cysteine ; tyrosine Toggle dot surface: |
glutamine (gln = Q) |
asparagine (asn = N) |
cysteine (cys = C) |
tyrosine (tyr = Y) |
|
Rotate 180o: glutamic acid ; aspartic acid ; arginine ; lysine ; histidine Toggle dot surface: |
glutamic acid (glu = E) |
aspartic acid (asp = D) |
arginine (arg = R) |
lysine (lys = K) |
histidine (his = H) |