Exam 2 Study Questions
Histology
Know the defining characteristics and functions of the major tissue types.
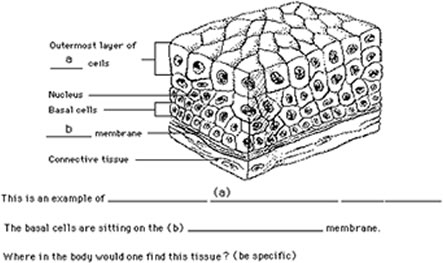
Be able to identify the tissue types based on a sketch or a description.
Epithelial tissue is classified on the basis of ___________ & ____________.
Connective tissue is classified on the basis of ___________ & __________.
The three types of muscle tissue are _________ , _________, and ______. ______
& ______ are striated, but _________ is not. __________ is "voluntary"
but _______ & _______ are not.
Intercalated discs are found in ____________. What is their function in that
tissue?
Densely packed collagen fibers are found in ____________ connective tissue.
(be specific)
Most glands are derived from _____________ tissue.
Simple squamous epithelium is found where __________ is important.
Joints are generally lined with ________ ___________, except in "heavy
duty" joints like the intervertebral discs where ________ _______ is found.
Fat storage is the primary function of __________ tissue.
_____________ ____________ is found in the internal lining of bladder.
What are the three types of cartilage? Where are they found?
Why is blood classified as a connective tissue?
What is the primary function of GAGs in cartilage?
Osteocytes and chondrocytes reside in spaces called____________.
Edema commonly occurs in ____________________ tissue. (be specific)
Fibroblasts are found in _______________________ tissue.
Nervous tissue is specialized for _____________________________.
The two cell types found in nervous tissue are _________ and ___________.
All cells in a simple epithelium are anchored to a structure called the _______
______.
The primary cell type found in cartilage is the _________________________.
The primary cell type found in areolar tissue is the ____________________.
Fibers of connective tissue may be ________________, __________________ or reticular.
The most abundant type of cartilage is ____________________________cartilage.
Integument
What are the key functions of the skin?
The pH of skin tends to be _________.
How is the skin “protective?” (there is more than one way!)
If given a diagram of the epidermis or the whole skin, be able to identify/label
the major layers and structures.
What are the four cell types found in the epidermis? What are their respective
functions?
Which layer of the epidermis is “optional?”
If given a diagram of the epidermis, be able to label the strata and associated
cell types.
If given a diagram of a hair follicle and associated structures (sebaceous gland,
arrector pili), be able to identify/label the major structures.
In which layer of the epidermis are melanocytes found? What is the function
of melanocytes? Melanocytes are different from keratinocytes -- explain.
Explain how the epidermis grows (or explain how the different epidermal layers
form).
What factors (cells, pigments) determine a person’s skin color?
What is trichosiderin?
What is keratin? What is its function and in what structures is it found?
What determines one’s hair color (besides genes and stuff you buy at the
drug store)?
What are two functions of the arrector pili? What controls the arrector pili?
What are the layers of the dermis?
What is the hypodermis? What the role of fat in the hypodermis?
What do ceruminous glands secrete?
What is sebum?
What is acne? Why does it increase during puberty?
What is a line of cleavage (or Langer’s line)?
What is a stretch mark? What causes them?
What is vitamin D? What is its function? How is it produced? Why is it often
considered to be a hormone rather than a vitamin? How does it relate to rickets?
Can adults get rickets? Why or why not?
What are positive and negative health aspects of sun exposure?
How does aging affect the skin?
Why is it unlikely that a person's hair would turn white overnight?
What is the basis of gray hair?
What is a decubitis ulcer and what causes one? (not in notes: see clinical applications
at end of chapter)
Why would an elderly person be more prone to decubitis ulcers?
List three effects of the sun on skin.
Hair growth is due to mitosis of cells within the __________.
What is a freckle?
What are the 3 types of skin cancer? How do they differ from one another? Which
is the most serious type and which is the least serious type? Why?
What is metastasis?
What is the “ABCD” method of diagnosing melanoma?
Is it possible to have a cancer of the stratum corneum? Why or why not?
What is male pattern baldness? Can women get male pattern baldness?
A man has filed a legal suit against the maker of minoxidyl (Rogaine), claiming
that it caused hair to grow on his palms. What is the major scientific flaw
in this case?
Propecia
(finasteride) is used to treat male pattern baldness. How does it work?
What is the difference been apocrine and eccrine sweat glands?
What is a pheromone?
What is the difference between a first, second and third degree burn? Why is
an extensive third degree burn life-threatening? (there are two key reasons).
Which type of burn requires skin grafts? Why?
What is the “rule of 9’s?”
Some drugs used to treat irregular heart rhythms block the action of the sympathetic
nervous system (see chapter 14). One side-effect of such drugs, e.g., atropine
or belladonna, is hyperthermia (over-heating) -- patients taking these drugs
are advised not to over exercise and to avoid hot tubs and spas. Why is there
a danger of hyperthermia for these patients?
Practice Questions
Matching: Match the description on the left with the tissue on the right. Answers
may be used more than once.
| _______ Single layer of square cells | A) simple squamous |
| B) pseudosimple | |
| _______ Found in linings of lung. | C) simple cuboidal |
| D) simple columnar | |
_______ Found in bladder lining |
E) pseudostratified |
| F) transitional epithelium | |
| _______ Forms collecting tubules of kidney | G) stratified squamous |
| H) stratified columnar | |
| _______ Voluntary and striated | I) stratified cuboidal |
| J) areolar connective | |
| _______ Forms dermis of skin | K) adipose |
| L) reticular connective | |
| _______ Matrix is plasma | M) dense irregular connective |
| N) dense regular connective. | |
| _______ Provides insulation for the body | O) elastic connective |
| P) hyaline cartilage | |
| _______ Found in intervertebral discs | Q) elastic cartilage |
| R) Fibrocartilage | |
| _______ Hard matrix is due to calcium salts | S) Blood |
| T) Bone | |
| _______ Has intercalated discs | U) Skeletal muscle |
| V) Cardiac muscle | |
| _______ Lining of the esophagus | W) Smooth muscle |
| X) Neurons | |
| _______ Allows aorta to stretch and recoil | Y) Supporting cells (glia) |
| Z) None of the above | |
| _______ Specialized for excitability | |
_______ Key tissue in lymph nodes |
|
_______ Ciliated variety found in trachea |
|
_______ Cells are long, cylindrical and multinucleate |
|
| _______ Non-striated and involuntary | |
| _______ Edema occurs in this tissue type |
List four tissues that have numerous collagen fibers.
The most abundant type of cartilage is ____________________________cartilage.
Osteocytes and chondrocytes reside in spaces called ________________________.
If joint capsules were constructed of dense regular connective tissue, what might be an advantage and a disadvantage of this?
