|
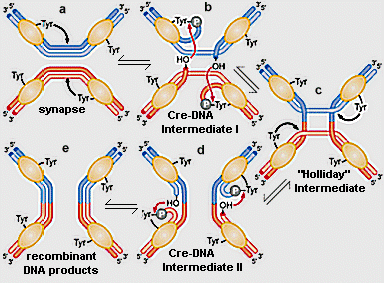
Figure 1. The site specific recombination reaction between two, lox DNA molecules (red and blue), catalyzed by Cre recombinase. (a) two Cre monomers bind to each lox site. A conserved, active site tyrosine (tyr324) from one of the monomers on each lox DNA molecule cleaves the DNA backbone, forming a covalent, 3' phosphotyrosine bond, leaving a free, 5' hydroxyl (OH) on one strand of each DNA double helix. (b) The 5' OH's perform a nucleophillic attack on the phophotyrosines from the partner DNA substrates, yielding a Holliday junction intermediate (c). (c)-(d) A second round of tyr324-catalyzed breakage, followed by strand joining reactions (nucleophillic attack of free OH's on phosphotyrosines) resolves the Holliday junction into recombinant products (e). Aadapted from Figure 11-8, Watson, et al., 2003, Molecular Biology of the Gene. |